#P3830. [SHOI2012] 随机树
[SHOI2012] 随机树
Description
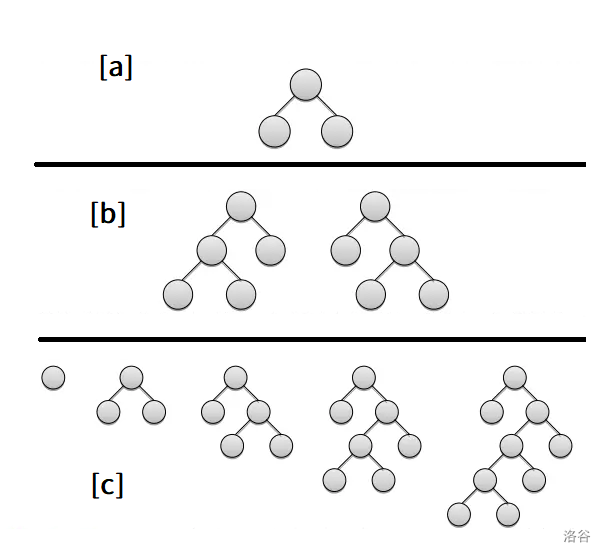
A binary tree with leaf nodes can be generated as follows. Initially there is only the root node. First, expand the root node (in this problem, “expand” means adding left and right children to a leaf node):
[a]
Then, uniformly at random choose one of the two leaf nodes to expand, i.e., generate one of the following two trees:
[b]
After that, at each step, uniformly at random choose one leaf node from all current leaf nodes and expand it.
Repeat this operation until there are leaf nodes. For example, a binary tree with leaf nodes might be generated by the following steps.
[c]
For a binary tree with leaf nodes generated by this process, find:
- The expected value of the average depth of the leaf nodes.
- The expected value of the tree depth. The root node is defined to have depth .
Input Format
The input contains one line with two positive integers , , representing the query type and the number of leaf nodes, respectively.
Output Format
Output one line with a real number , rounded to digits after the decimal point. If , then is the expected value of the average depth of the leaf nodes; if , then is the expected value of the tree depth.
1 4
2.166667
2 4
2.666667
1 12
4.206421
2 12
5.916614
Hint
【Explanation for Samples 1 and 2】 The expected value of a random variable is the sum of each value times its probability. Let the possible values of random variable be , and their probabilities be . Then the expected value of is .
For example, when rolling a fair die labeled with the numbers , the expected value of the outcome is: $E=\frac{1}{6}\times 1+\frac{1}{6}\times 2+\frac{1}{6}\times 3+\frac{1}{6}\times 4+\frac{1}{6}\times 5+\frac{1}{6}\times 6 = 3.5$, even though is not one of the die faces. As another example, consider a single-choice question with options: a correct answer gives points, no answer gives points, and a wrong answer gives point. If we do not answer, we certainly get ; if we guess uniformly at random, the expected score is: $E=\frac{1}{4}\times 5+\frac{1}{4}\times (-1)+\frac{1}{4}\times (-1)+\frac{1}{4}\times (-1)=\frac{1}{2}$.
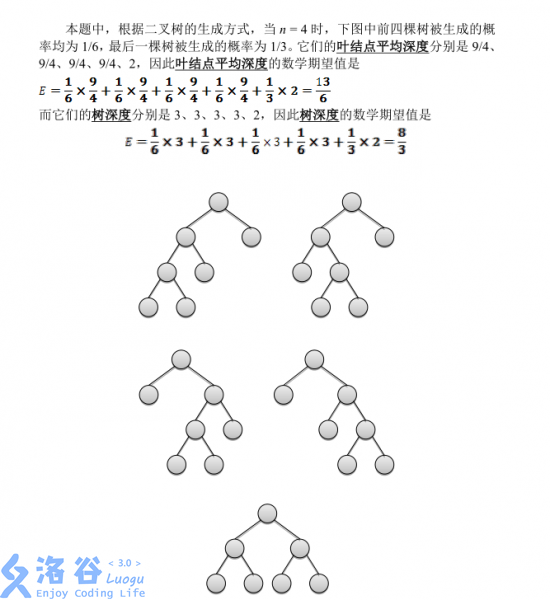
In this problem, according to the generation process, when , in the figure below the first four trees are generated with probability each, and the last tree with probability . Their average leaf depths are , , , , , so the expected value of the average leaf depth is $E=\frac{1}{6}\times \frac{9}{4}+\frac{1}{6}\times \frac{9}{4}+\frac{1}{6}\times \frac{9}{4}+\frac{1}{6}\times \frac{9}{4}+\frac{1}{3}\times 2=\frac{13}{6}$. Their tree depths are , so the expected value of the tree depth is $E=\frac{1}{6}\times 3+\frac{1}{6}\times 3+\frac{1}{6}\times 3+\frac{1}{6}\times 3+\frac{1}{3}\times 2=\frac{8}{3}$.
Constraints | Testdata ID | | | | ---- | ---- | ---- | | 1, 2 | | | | 3, 4, 5 | | | | 6, 7 | | | | 8, 9, 10 | | |

Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号