#P3576. [POI 2014] MRO-Ant colony
[POI 2014] MRO-Ant colony
Description
Ants searching for food have come to a mountain.
This mountain has caves and roads connecting these caves. In other words, all caves and roads form a tree.
For each cave that is connected by exactly one road, there is an entrance that connects that cave to the outside.
At each entrance, there are swarms of ants. The size of the -th swarm is .
The swarms enter the mountain one after another; the next swarm enters if and only if there are no ants in the mountain.
Once inside, the ants move as follows:
- If a swarm enters a cave that is connected to roads (excluding the road they used to enter this cave), then the swarm splits into swarms of equal size, and each swarm chooses one road so that each road is taken by exactly one swarm. In particular, if (i.e., the swarm reaches an exit), the ants leave the mountain through that exit.
- According to the above, if this swarm has ants, then each of the swarms has ants, and the remaining ants disappear (how they disappear is not important :)).
The figure below shows an example: a swarm of size arrives at a cave that has roads (other than the one they came from), and the swarm splits into three swarms of size each.
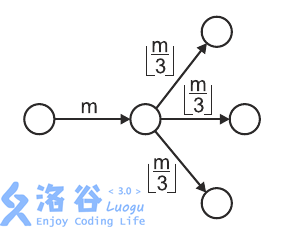
On one of the roads, there is an anteater. Whenever a swarm passing along that road has size exactly , it eats that entire swarm.
Now, please compute how many ants the anteater eats in total.
Input Format
The first line contains three integers .
The next line contains integers .
Then follow lines, each containing two integers , indicating that there is an edge between and .
The first edge in the input is the edge where the anteater is located.
Output Format
Output a single integer, the sum of the sizes of all eaten swarms.
7 5 3
3 4 1 9 11
1 2
1 4
4 3
4 5
4 6
6 7
21
Hint
For of the testdata, , , .
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号