#P2354. [NOI2014] 随机数生成器
[NOI2014] 随机数生成器
Description
Little H is studying randomized algorithms. Randomized algorithms often obtain randomness by calling random number generator functions (for example, random in Pascal and rand in C/C++). In fact, such functions are not truly “random”; they are usually computed by some algorithm.
For example, the following quadratic polynomial recurrence is a common algorithm:
Choose non-negative integers as the random seed, and compute using the following recurrence.
For any , $x_i = (a \times x_{i-1}^2 + b \times x_{i-1} + c) \mod d$. In this way we can obtain a non-negative integer sequence of arbitrary length , and generally we regard this sequence as random.
Using the random sequence , we can generate a random permutation of to , denoted , by the following algorithm:
- Initialize as the increasing sequence to .
- Perform swaps. At the -th swap, exchange the values of and .
In addition, on top of these swaps, Little H performs extra swap operations. For the -th extra swap, Little H chooses two indices and , and swaps the values of and .
To test the practicality of this random permutation generation algorithm, Little H designs the following problem:
Little H has a board with rows and columns. First, following the above process, after swap operations, she generates a random permutation of , denoted . Then she fills these numbers into the board row by row and column by column in order: that is, the number filled in the cell at row , column is .
Next, Little H wants to start from the top-left corner of the board, i.e., the cell at row , column . Each move goes either right or down, and without leaving the board, she reaches the bottom-right corner, i.e., the cell at row , column .
Little H records the numbers on all visited cells, and sorts them in ascending order. Thus, for any valid path, Little H can obtain an increasing sequence of length , which we call the path sequence.
Little H wants to know what the lexicographically smallest path sequence she can obtain is.
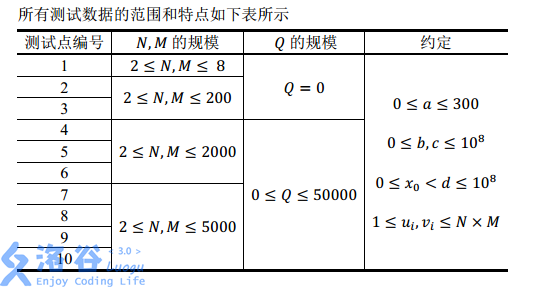
Input Format
The first line contains integers , describing the random seed required by Little H’s random number generation algorithm.
The second line contains three integers , indicating that Little H wants to generate a permutation of to to fill her -row -column board, and that after the initial swap operations, she performs extra swap operations.
The next lines each contain two integers , indicating that at the -th extra swap operation, the values of and are swapped.
Output Format
Output one line containing positive integers separated by spaces, representing the lexicographically smallest path sequence that can be obtained.
1 3 5 1 71
3 4 3
1 7
9 9
4 9
1 2 6 8 9 12
654321 209 111 23 70000001
10 10 0
1 3 7 10 14 15 16 21 23 30 44 52 55 70 72 88 94 95 97
123456 137 701 101 10000007
20 20 0
1 10 12 14 16 26 32 38 44 46 61 81 84 101 126 128 135 140 152 156 201 206 237 242 243 253 259 269 278 279 291 298 338 345 347 352 354 383 395
Hint
For Sample 1, according to the input seeds, the first random numbers that Little H obtains are:
9 5 30 11 64 42 36 22 1 9 5 30
Based on these random numbers, after the initial swap operations, Little H obtains the permutation:
6 9 1 4 5 11 12 2 7 10 3 8
After the additional swap operations, Little H obtains the final random permutation:
12 9 1 7 5 11 6 2 4 10 3 8
12 9 1 7
5 11 6 2
4 10 3 8
The optimal path passes through the numbers: 12-9-1-6-2-8.
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号