#P1267. 排序二叉树
排序二叉树
Description
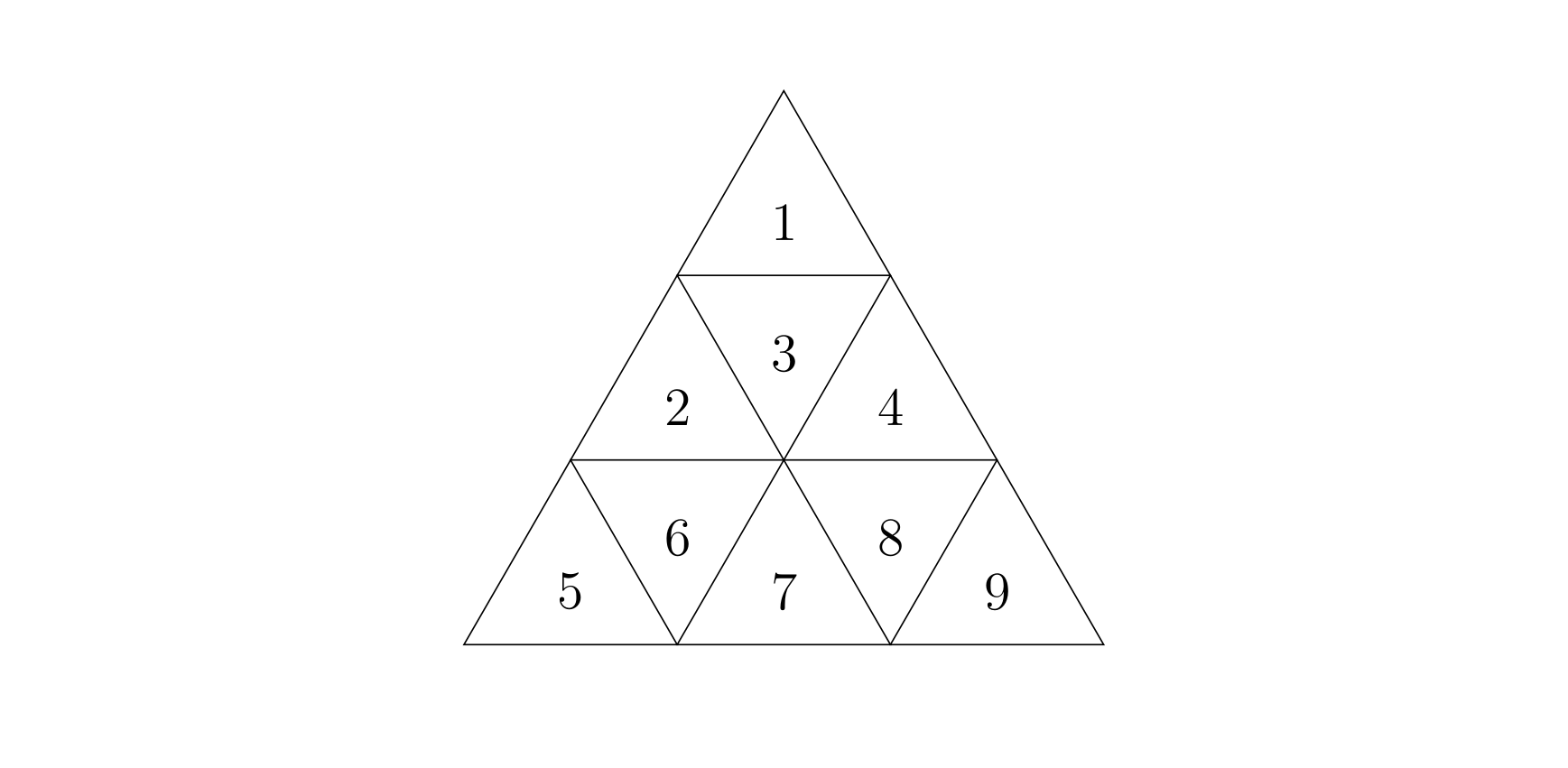
An equilateral triangle with side length can be partitioned into small equilateral triangles of side length , called unit triangles. An equilateral triangle with side length is divided into three layers for a total of small triangles, which we number from top to bottom and left to right; see the figure below.
Four such equilateral triangles of side length can form a regular tetrahedron. We number the three side faces of the tetrahedron, in clockwise order as seen from top to bottom, as , and the base as . On side faces , triangle has the tetrahedron’s apex as its top vertex; on the base face , triangle has as its top vertex the point where it meets faces and .
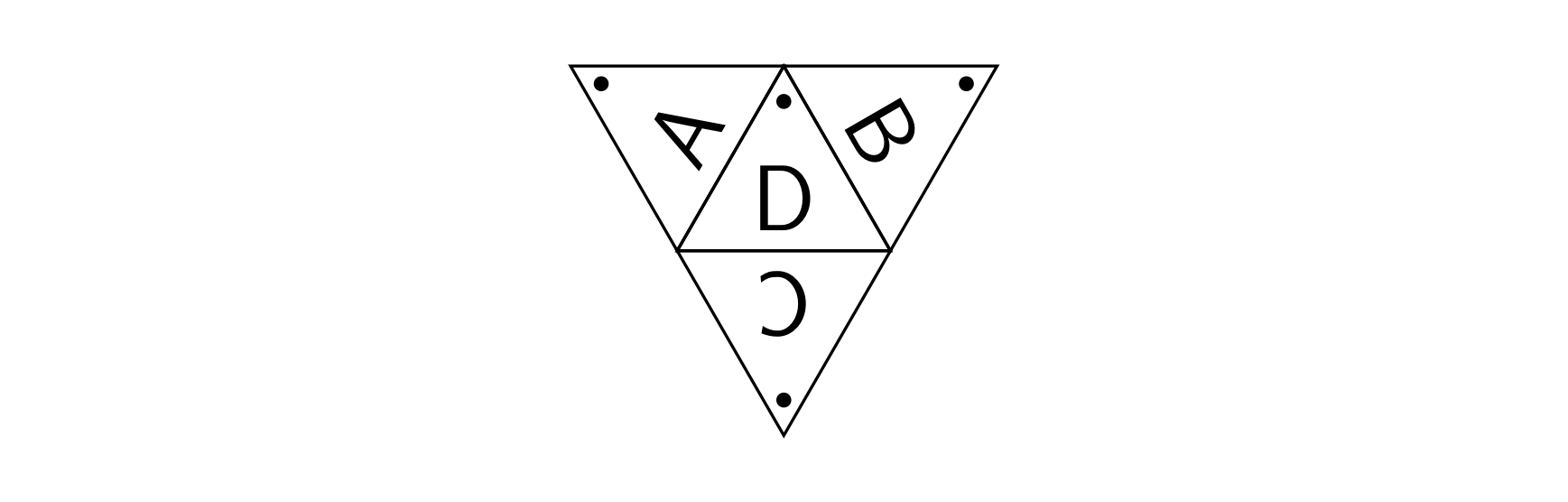
Here, marks the position of triangle on that face, and the rest are numbered in order accordingly.
The above is the unfolded net of the tetrahedron. The dotted point on each face marks that face’s top vertex. Folding side faces inward reconstructs the tetrahedron. We partition each face into unit triangles.
Two unit triangles are adjacent if they share an edge. Clearly, each unit triangle has three adjacent unit triangles. Now, place all integers from to randomly into the unit triangles across the four faces, one number per unit triangle.
You are to compute the maximum binary search tree formed by unit triangles. The maximum binary search tree is the one with the largest number of nodes among all binary search trees formed by unit triangles. The requirement is that when is a node of the binary search tree, its children (if any) and its parent (if any) must be adjacent to by a shared edge in the folded tetrahedron (not adjacency in the unfolded net).
A binary search tree satisfies that every value in a node’s left subtree is strictly less than that node’s value, and every value in the right subtree is strictly greater than that node’s value.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer , the side length of each triangular face in the unfolded net, i.e., each face has unit triangles.
Then follow four lines, each containing integers: the first line gives the numbers on face , the second on face , and so on.
Output Format
Output a single integer, the number of nodes in the maximum binary search tree.
3
19 33 32 31 29 3 5 4 30
22 25 20 21 12 24 23 34 35
14 13 15 26 18 17 8 16 27
11 10 9 1 28 7 2 6 36
17
Hint
Sample explanation
Take face as an example. Let denote the -th unit triangle on face , and similarly for other faces.
is adjacent to , is adjacent to , and is adjacent to .
is adjacent to , is adjacent to , and is adjacent to .
is adjacent to , is adjacent to , and is adjacent to .
Taking the number as the root, one maximum binary search tree is:

Constraints
For of the testdata, . All numbers on the four faces are distinct and are drawn from .
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号