#P12535. [XJTUPC 2025] 棱堡
[XJTUPC 2025] 棱堡
Description
A bastion is the first type of fortress that relies solely on direct firepower and has no attack blind spots.

A simple non-degenerate polygon is a closed polygonal composed of a sequence of () vertices, satisfying the following conditions:
- The vertex sequence connects end to end, forming edges, constituting a compact closed set in the plane (including all boundary and interior points);
- The edges only meet at the vertices and do not intersect each other (adjacent edges have no other intersection points outside the common vertex);
- The vertices are distinct, not located inside any non-adjacent edges, and any three consecutive vertices are not collinear.
The bastion can be viewed as a simple non-degenerate polygon composed of points and edges. For two distinct points and on the edges of the polygon, we define that point can directly fire at point if and only if the line segment intersects the polygon only at points and . As shown in the figure below, points and cannot directly fire at point , but point can. If there is a point on the edge of the polygon such that there is no other point on the edge of the polygon for which point can directly fire at , then we call point a fire blind spot of the polygon.
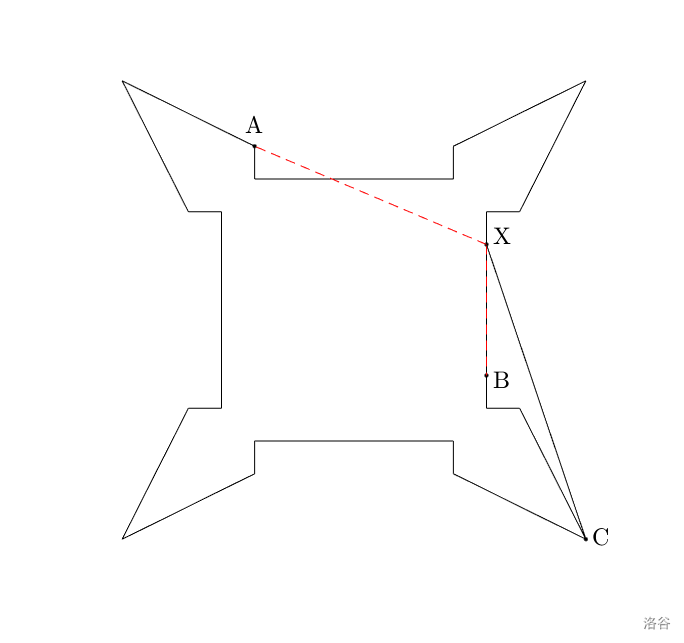
We call a simple non-degenerate polygon a bastion if and only if it has at most a finite number of points that are fire blind spots. Given a simple non-degenerate polygon, please determine whether it is a bastion.
Formally, given a simple non-degenerate polygon, please determine whether there are only a finite number of points located on the edges of the polygon such that there is no other point on the edges of the polygon for which the line segment intersects the polygon only at points and .
Input Format
The input contains multiple test cases. The first line of the data contains an integer () indicating the number of test cases. The following describes each test case.
The first line of each test case contains an integer (), which is the number of edges of the polygon.
The next lines each contain two integers and (), describing a vertex of the polygon.
The input data guarantees that a simple non-degenerate polygon is formed. The vertices are given in counterclockwise order, that is, after traversing all the vertices in order, it rotates exactly counterclockwise. Connect edges in sequence according to the input order of the vertices (the -th vertex is connected to the -th vertex, and the -th vertex is connected back to the -st vertex).
It is guaranteed that the sum of for all test cases does not exceed .
Output Format
For each test case, output a single line containing a string. If the polygon is a bastion, output ; otherwise, output . The answer is case insensitive.
2
20
7 5
9 5
13 13
5 9
5 7
-5 7
-5 9
-13 13
-9 5
-7 5
-7 -5
-9 -5
-13 -13
-5 -9
-5 -7
5 -7
5 -9
13 -13
9 -5
7 -5
4
1 1
-1 1
-1 -1
1 -1
YES
NO

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号