#P4532. [CTSC2005] 合并正方形
[CTSC2005] 合并正方形
Description
A two-dimensional plane is initially empty. There is a sequence of commands that add points to the plane.
There are two kinds of points, called type A points and type B points (see Figure 1, where black squares denote type A points and small black dots denote type B points). Type A points always lie on the -axis and never overlap, while type B points can appear anywhere on the plane and may overlap. Each type B point has a weight .
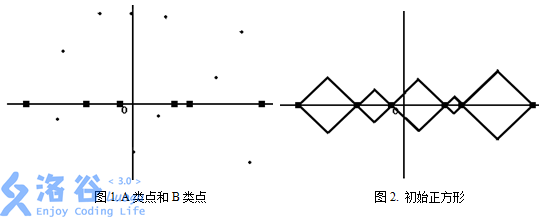
Processing: (1) Initially, between every pair of adjacent type A points, draw a square whose sides make a -degree angle with the -axis (see Figure 2). (2) Each time, you may merge any two squares that share at least one common point into a larger square; after merging, the two smaller squares disappear. The second and third squares from the left in Figure 2 are merged and shown as the gray-edged square in Figure 3.

After merging, the resulting square divides the plane into regions. The regions adjacent to the sides of the square are labeled I, II, III, IV in Figure 3. Let be the sum of weights of type B points falling into region I, for region II, for region III, and for region IV. Let be the sum of weights of type B points falling inside the gray square (type B points are guaranteed not to lie on the boundaries of any region). Then the cost of this merge is . Type B points in other regions are ignored. Each merge does not affect the positions or weights of the type B points.
Each time you perform a merge, the number of squares formed by type A points decreases by one, until only one square remains. The total merge cost is the sum of the costs of all merges. Different merge orders may result in different total costs.
Points are added to the plane one by one. After adding the -th type A point, the plane contains type A points and all previously added type B points. Let the minimum total merge cost at this moment be .
Given a cost limit , compute the maximum number of type A points such that the minimum total merge cost for the first type A points does not exceed , i.e., .
Input Format
The first line contains two numbers , , meaning there are add-point commands and the cost limit is .
Then follow lines, each starting with a letter indicating the point type. A denotes a type A point, and B denotes a type B point. For a type A point, one number follows giving its -coordinate; for a type B point, three numbers follow giving its -coordinate, -coordinate, and weight.
Output Format
Output a single integer , which is the largest such that .
8 30.0
A -2
A 0
B 7 8 5.0
B 4 -3 2.0
B -3 4 1.0
A 2
B -4 5 1.0
A 4
3
Hint
Sample explanation:
In the state after adding the last point, all points are as shown below. The number next to each type B point is its weight.
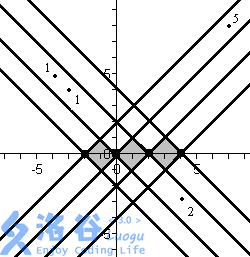
The minimum cost for the first type A points is , and for the first type A points is . Since and , the maximum is .
Constraints:
- .
- .
- , are integers with absolute value at most .
- , are real numbers with , ; all input real numbers have at most three decimal places.
- of the testdata satisfies .
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号