#P3721. [AHOI2017/HNOI2017] 单旋
[AHOI2017/HNOI2017] 单旋
Description
The Kingdom of H is a nation passionate about coding. People there go to school from a young age to learn all kinds of data structures. The splay tree (splay) is a data structure that is easy to implement, feature-rich, and efficient; mastering it is a required skill in the Kingdom of H. One day, the evil "Ka" (Kǎ) came with his evil "constant factor" to try to destroy the kingdom. "Ka" brainwashed the people of H by saying that if a splay is implemented using only single rotations, it would be faster. "Ka" called this "single-rotation splay" a "spaly". Although this makes little sense, some people in H believed him—Little H was one of them—and "spaly" immediately became his faith. The king of H, of course, would not allow such a trend to spread. The king constructed a piece of testdata consisting of (no more than ) operations. He knows this testdata will surely defeat spaly, but the king has many other things to do, so the task of computing the actual cost of each operation is handed over to you.
There are types of operations in the testdata:
-
Insert: Insert a new isolated node with key into the current non-empty spaly. The insertion method is: first compare with the root. If is smaller than the root, go to the left subtree; otherwise go to the right subtree. Repeat this until, at some point, is smaller than the current subtree root and ’s left subtree is empty—then make the left child of ; or is larger than the current subtree root and ’s right subtree is empty—then make the right child of . The cost of this operation is: the depth of after insertion. In particular, if the tree is empty, directly make the new node the entire one-node tree. (All keys are distinct. For the definition of “depth,” see the spaly description at the end.)
-
Single-rotate minimum: Single-rotate the element with the minimum key in the spaly to the root. The operation cost is: the depth of before the single rotation. (For single rotation, see the spaly description at the end.)
-
Single-rotate maximum: Single-rotate the element with the maximum key in the spaly to the root. The operation cost is: the depth of before the single rotation.
-
Single-rotate delete minimum: First perform operation 2, then delete the root. After operation 2, the root has no left subtree, so simply replace the root with its right subtree (see the sample explanation for details). The operation cost is the same as in operation 2.
-
Single-rotate delete maximum: First perform operation 3, then delete the root. The operation cost is the same as in operation 3.
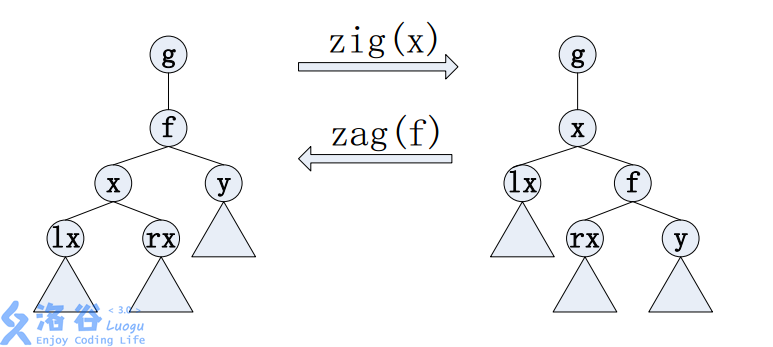
If you are not from the Kingdom of H, you may need to know some spaly knowledge to complete the king’s task:
-
A spaly is a binary tree that satisfies: for any node , if it has a left child , then the key of is less than the key of ; if it has a right child , then the key of is greater than the key of .
-
The depth of a node in a spaly is defined as: the number of nodes on the path from the root to that node (including itself).
-
The single rotation operation is defined for a node in a tree. Initially, let be the parent of in the tree. If is the left child of , then perform zig(x) (as in the figure above, the left tree becomes the right tree after zig(x)); otherwise perform zag(x) (in the figure above, applying zag(f) to the right tree turns it back into the left tree). Each time you perform zig(x) or zag(x), the depth of decreases by . Repeat this until becomes the root. In short, single-rotating means repeatedly performing zig and zag to make the root.
Input Format
The input file is named splay.in.
The first line contains a single positive integer ().
Then follow lines, each describing an operation: first an operation code (), which is one of the types above. If , then an additional non-negative integer is given, representing the key of the newly inserted node.
Output Format
The output file is named splay.out.
Output lines, one integer per line. The -th line corresponds to the cost of the -th input operation.
5
1 2
1 1
1 3
4
5
1
2
2
2
2
Hint
of the testdata satisfies: .
Additionally, of the testdata satisfies: operations 4 and 5 do not appear.
of the testdata satisfies: , . All keys that appear are distinct. For any non-insert operation, the tree is guaranteed to be non-empty. Before any operation, the tree is empty.
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号