#P3521. [POI 2011] ROT-Tree Rotations
[POI 2011] ROT-Tree Rotations
Description
You are given a binary tree with leaves. Each leaf has a weight (note: the root is not a leaf), and the weights of all leaves form a permutation of .
For any node in this binary tree, it is guaranteed that it is either a leaf, or it has both left and right children.
You may choose any set of nodes and swap their left and right subtrees.
On the final tree, perform a preorder traversal of the whole tree and record the weights of the encountered leaves to form a permutation of length . You need to minimize the number of inversions of this permutation.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer , the number of leaves.
In the following lines, the tree is read recursively. When reading any subtree, start with its root. For a node , first read an integer on a separate line.
- If , then is a leaf and its weight is .
- If , then is an internal node; next read the information of its left subtree, and then the information of its right subtree.
Output Format
Output a single integer, the minimal number of inversions.
3
0
0
3
1
2
1
Hint
Explanation for Sample 1:
In the figure below, the left is the initial tree, and the right is the tree after the operations.
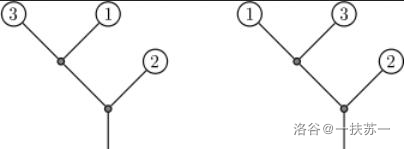
Constraints:
- For of the testdata, .
- For of the testdata, , , and the weights of all leaves form a permutation of .
Note: Please note that is not the number of nodes in the tree.
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号