#P2316. [HNOI2005] 分形
[HNOI2005] 分形
Description

A fractal has a fractional dimension, between and . A complete fractal picture often has a bounded area and an infinite perimeter. To explore the secrets of fractals, King persistently conducts an unconventional study.
He first studies a simple fractal: In the plane, there is a circle of radius () centered at the origin. It is externally tangent to several circles of radius . Each circle of radius is externally tangent to several circles of radius , …, and each circle of radius is externally tangent to several circles of radius . Any two circles do not intersect, do not overlap, are not contained one in another, and are not internally tangent. A circle of radius can only be externally tangent to circles of radius or , and for it is externally tangent to exactly one circle of radius .
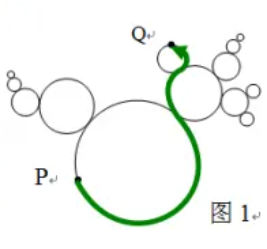
As a foundation, he first studies a finite-layer simple fractal, that is, an -layer fractal composed only of circles with radii through . Figure 1 shows a -layer simple fractal. Since there are only finitely many layers, the boundary length is finite.
On the boundary, King identifies several pairs of points related to the properties of the fractal picture. From to , what is the length of the shortest smooth path (see the bold curve in Figure 1).
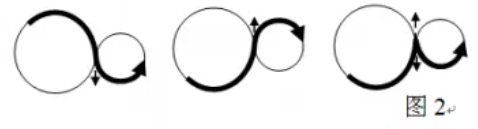
A smooth path means: at a common tangent point of two circles, when the path turns, its tangent direction remains unchanged. In Figure 2, the two bold paths on the left are smooth, while the bold path on the right is not smooth.
Input Format

The first line contains integers . Here is the number of circles (and the circles are numbered through ), and is the number of special point pairs.
The second line contains positive integers through .
Each of the next lines describes a circle. Each line contains numbers . is the center of circle . The radius of circle is . The index of the larger circle tangent to circle is . and may be real numbers.
Each of the next lines describes a special pair of points. Each line contains numbers , which specify the locations of a special pair :
- means point lies on circle , and with the center of this circle as the origin, its argument (angle) is .
- means point lies on circle , and with the center of this circle as the origin, its argument (angle) is .
Output Format

For each special pair, output one line containing one integer, which is the shortest length divided by , rounded to the nearest integer.
1 3 3
50000
0 0 0 0
150000 0 1 1
0 150000 1 1
3 5.497787 2 2.356194
3 1.570796 2 0.0
3 0.0 2 1.570796
175000
150000
200000
Hint
For of the testdata:
- .
- .
For of the testdata:
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- Any two circles are either externally tangent or disjoint.
- All special points are not points of tangency.
- Each circle is externally tangent to at most circles.
- All real numbers have at most decimal places.
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号