#P2146. [NOI2015] 软件包管理器
[NOI2015] 软件包管理器
Description
You decide to design your own package manager. Inevitably, you must handle dependencies between packages. If package depends on package , then before installing package , you must first install package . Likewise, if you want to uninstall package , you must uninstall package .
Now you have obtained all dependency relations among packages. Moreover, due to your previous design, every package in your manager except package depends on exactly one package, and package depends on none. The dependency relations contain no cycles (i.e., there do not exist packages such that for , depends on , and depends on ).
You now need to write a dependency resolver for your package manager. According to user feedback, when installing or uninstalling a package, users want to quickly know how many packages will actually change their installation state as a result of the operation (that is, how many currently uninstalled packages will be installed by an install operation, or how many currently installed packages will be uninstalled by an uninstall operation). Your task is to implement this part.
Note that installing an already installed package, or uninstalling a package that is not installed, will not change any installation state. In this case, the number of packages whose installation state changes is .
Input Format
The first line contains a positive integer , the number of packages, numbered starting from .
The second line contains integers; the -th integer denotes the package ID that package depends on.
Then a line with a positive integer follows, denoting the number of operations, in the following format:
install xmeans install package .uninstall xmeans uninstall package .
Initially, all packages are not installed.
For each operation, you need to output how many packages will change their installation state because of this step, and then apply the operation (i.e., update the installation states you maintain).
Output Format
Output lines, each containing an integer, which is the answer for each query.
7
0 0 0 1 1 5
5
install 5
install 6
uninstall 1
install 4
uninstall 0
3
1
3
2
3
10
0 1 2 1 3 0 0 3 2
10
install 0
install 3
uninstall 2
install 7
install 5
install 9
uninstall 9
install 4
install 1
install 9
1
3
2
1
3
1
1
1
0
1
Hint
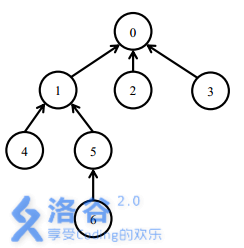
Initially, all packages are not installed.
To install package , you need to install packages .
After that, installing package only requires installing package . At this point, packages are installed.
Uninstalling package requires uninstalling packages . Now only package remains installed.
Next, installing package requires installing packages . Now packages are installed. Finally, uninstalling package will uninstall all packages.
Constraints
::cute-table{tuack}
| Test point ID | $$n$$ size | $$q$$ size | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ^ | |||
| testdata does not include uninstall operations | |||
| ^ | |||
| For package , the ID of the package it depends on is uniformly random in , and the package ID in each operation is uniformly random in . | |||
| ^ | |||
| ^ | |||
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号