#P1864. [NOI2009] 二叉查找树
[NOI2009] 二叉查找树
Description
You are given a special binary search tree (BST). By definition, in this BST the data value of each node is greater than the data value of its left child and less than the data value of its right child.
On the other hand, every node in this tree also has a weight, and the weight of each node is smaller than the weights of its children.
All data values in the tree are distinct, and all weights are also distinct. From this, we get an interesting conclusion: if the data value and the weight of every node are known, then the structure of the tree is uniquely determined. Equivalently, such a tree can be seen as the BST ordered by data values, obtained by inserting nodes in increasing order of weight.
The depth of a node in the tree is defined as its distance to the root plus . Therefore, the depth of the root is .
Besides the data value and the weight, each node also has an access frequency. We define the access cost of a node to be its access frequency multiplied by its depth. The total access cost of the tree is the sum of the access costs of all nodes.
Now you are given the data value, weight, and access frequency of every node. You may modify the weights of some nodes as needed, but each modification incurs an extra modification cost of . You may change a node’s weight to any real number, but after all modifications the weights must remain pairwise distinct. Your task is to determine the minimum possible value of the sum of the total access cost of the tree and the extra modification cost.
Input Format
The first line contains two positive integers , where is the number of nodes and is the extra cost incurred by each modification.
The next line contains non-negative integers, the data values of the nodes.
The following line contains non-negative integers, the weights of the nodes.
The next line contains non-negative integers, the access frequencies of the nodes.
All data values, weights, and access frequencies do not exceed .
Output Format
Output a single line containing one number: the minimum possible sum of the total access cost and the extra modification cost.
4 10
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
29
Hint
Sample explanation:
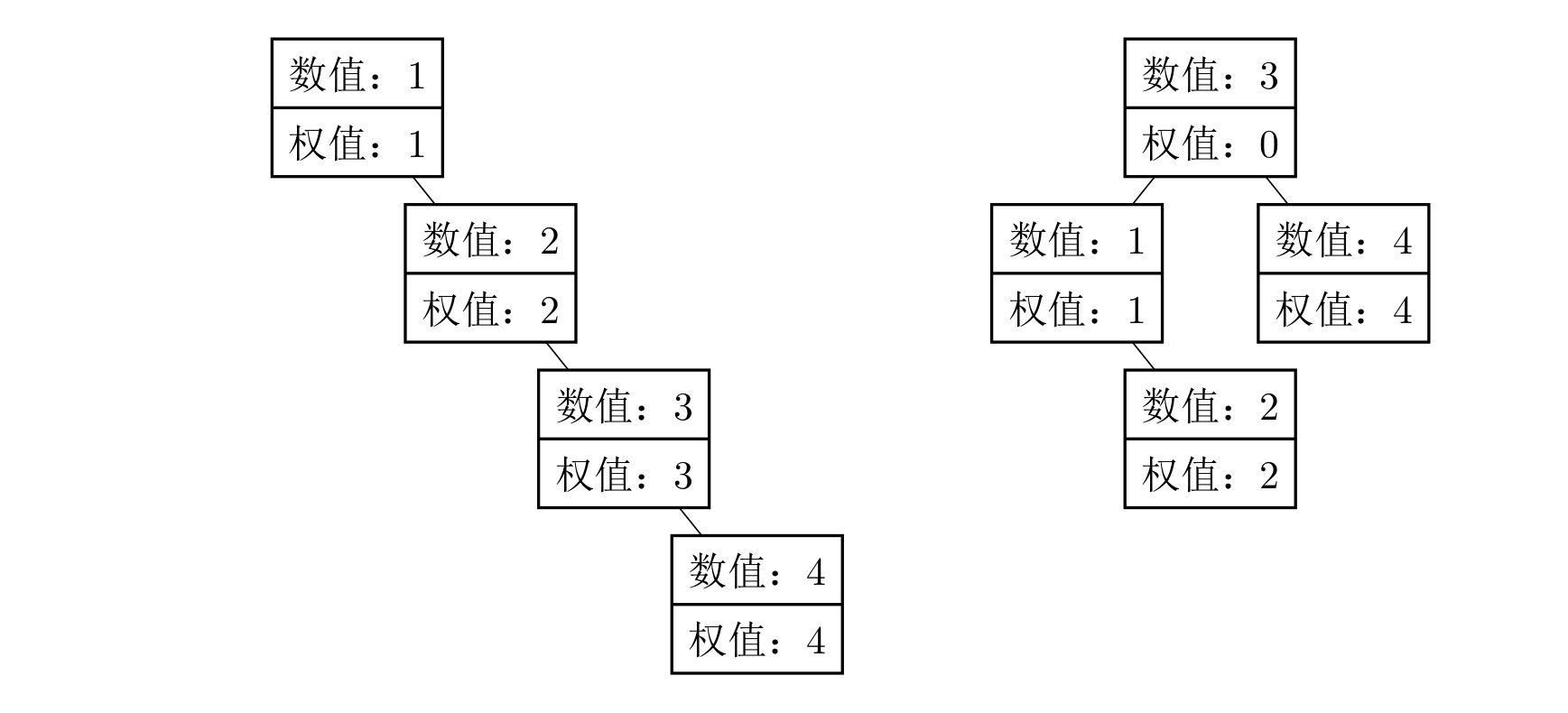
The original tree from the input is shown on the left, and its access cost is $1 \times 1 + 2 \times 2 + 3 \times 3 + 4 \times 4 = 30$.
The optimal modification is to change the weight of the rd node to , yielding the tree on the right. Its access cost is $1 \times 2 + 2 \times 3 + 3 \times 1 + 4 \times 2 = 19$. Adding the extra modification cost gives a total of .
Constraints:
- For of the testdata, .
- For of the testdata, .
- For of the testdata, , .
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号