#P11762. [IAMOI R1] 走亲访友
[IAMOI R1] 走亲访友
Description
Xiao C has relatives connected by bidirectional roads, ensuring all relatives are mutually reachable.
Xiao C will personally visit them starting from the -th relative's home. Each time she can move to a relative's home connected by a road. However, whenever she traverses a road, admirers swarm in causing congestion. She can choose to hide her charm (marking ) to prevent congestion, otherwise (marking ) the road becomes permanently blocked after this traversal.
Xiao L is bad with directions, so Xiao C wants to leave exactly unblocked roads forming a connected tree, while traversing at most roads. Construct such a traversal plan.
Formal Problem Statement
Given a simple undirected connected graph with nodes and edges, construct a path satisfying:
- Starts at node (end node unrestricted).
- For each traversed edge , assign where:
- : Delete this edge (cannot be reused).
- : Keep this edge.
- Path continuity: for (even if edge is deleted).
- Path length ≤ .
- Remaining edges form a spanning tree.
Multiple traversals allowed before deletion. Solution always exists under given constraints.
Input Format
- First line: four integers , , , .
- Next lines: two integers and per line, representing a bidirectional road.
Output Format
- First line: integer (number of traversed edges).
- Next lines: two integers per line - edge index (1-based input order) and (0/1).
Any valid solution is accepted.
5 5 10 4
1 3
2 5
2 3
4 5
1 5
2
4 1
2 0
Hint
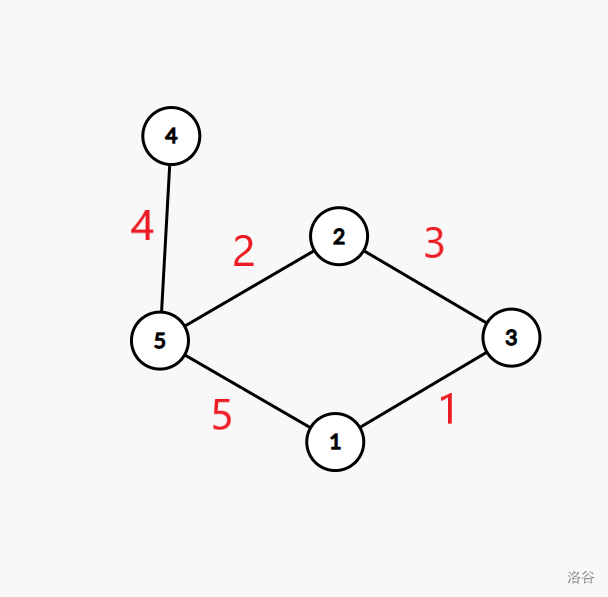
After traversing edge 4 (keep) to node 5, then edge 2 (block), remaining edges form a tree. Alternative solutions like
2
4 1
5 0
or
3
4 1
2 1
3 0
are also valid.
Constraints
Subtask scoring
| Subtask | Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | ≤10 | 100 | 20 |
| 2 | 100 | ≤ | 10 | |
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ≤ | 20 | ||
| 5 | 40 |
For 100% data:
- No self-loops or duplicate edges
Postscript: This is a modified version. The original problem remains unsolved. Contact Down_syndrome for ideas.
Translation by DeepSeek R1

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号