#P1023. [NOIP 2000 普及组] 税收与补贴问题
[NOIP 2000 普及组] 税收与补贴问题
Description
You are a project manager at a consulting firm. You already know the government's expected price for a certain product, as well as its sales at various price points. You are required to determine the minimum amount (also an integer) of tax to collect or subsidy to grant on this product so that, at the government's expected price, the seller achieves the maximum total profit compared with all other price points.
- Total profit profit per unit sales.
- Profit per unit unit price unit cost (minus tax or plus subsidy).
Input Format
- The first line is the government's expected price for the product.
- The second line contains two integers: the first is the product's cost, and the second is the sales volume when sold at cost price.
- Then follow several lines, each containing two integers: the first is the unit price at some price point, and the second is the sales volume at that price. A line
-1 -1indicates that all known price points and their corresponding sales have been entered. - The last line contains a single integer indicating the decrease in sales for each 1 yuan increase in price beyond the highest known unit price.
Output Format
There are two cases:
- If the maximum total profit can be achieved at the government's expected price, output a single integer. Its sign indicates whether it is a subsidy or a tax, and its absolute value is the minimum amount. If there are multiple solutions, output the one with the smallest absolute value.
- If the maximum total profit cannot be achieved at the government's expected price, output
NO SOLUTION.
31
28 130
30 120
31 110
-1 -1
15
4
Hint
Constraints and Conventions
All input numbers are less than .
Sample Explanation (updated on 2023/6/22)
The following figure shows the price–sales curve corresponding to the sample input. The horizontal axis represents the selling price, and the vertical axis represents the sales volume.
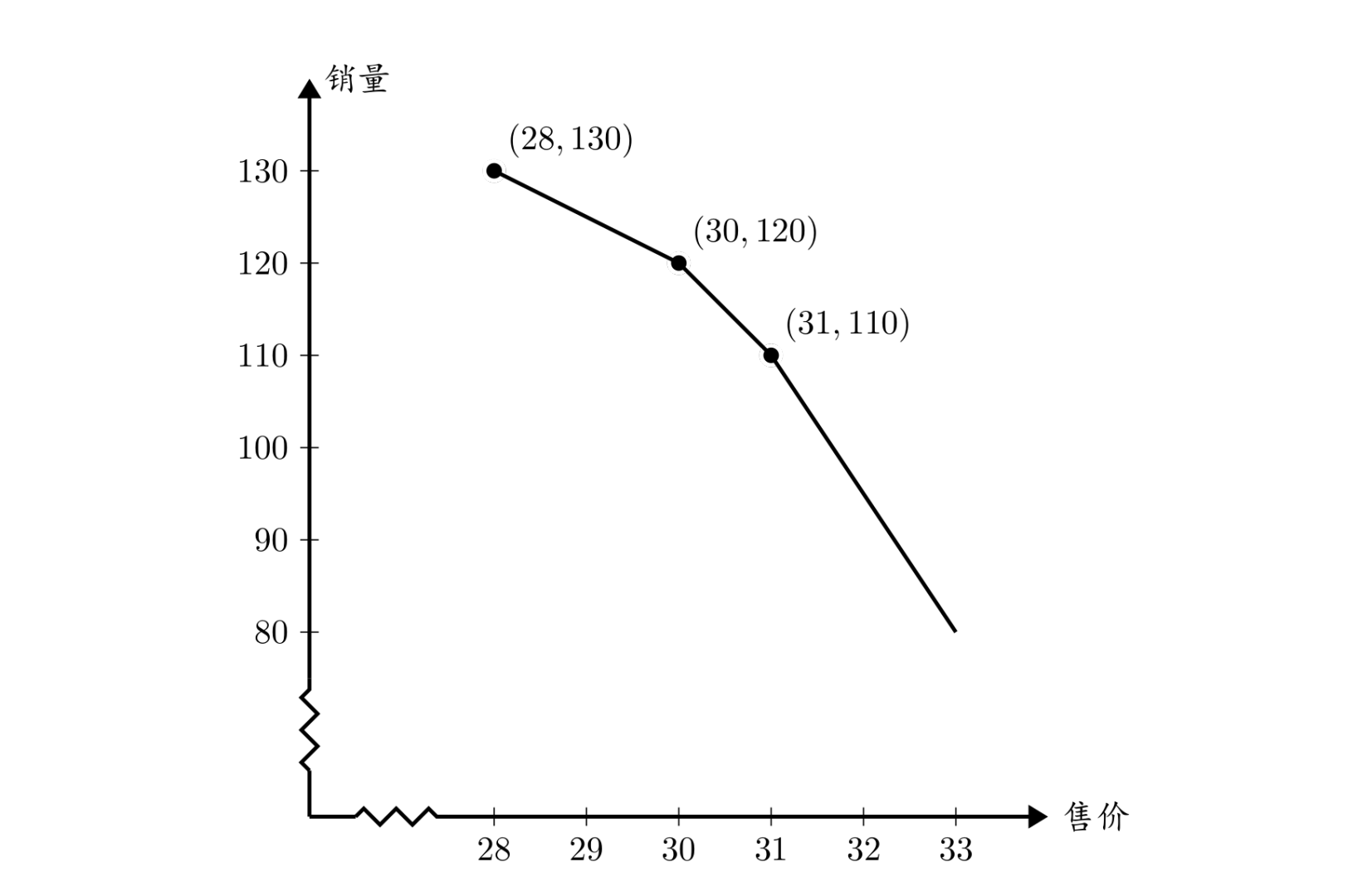
According to the problem statement, the cost is yuan. The selling price should not be lower than yuan. When the selling price exceeds the maximum given price yuan, the sales decrease by for each 1 yuan increase in price. For example, when the selling price is yuan, the sales are . Between the given price points, the sales change linearly.
When the government provides a subsidy of yuan for this product and the firm sets the price at yuan, the profit is yuan per unit, the sales are units, and the total profit is yuan, which is the maximum total profit the firm can obtain among all pricing choices. In this case, the firm's selling price matches the government's expected price, so this is a valid solution.
Translated by ChatGPT 5

 京公网安备 11011102002149号
京公网安备 11011102002149号